The Power of Diagnostic Imaging for Prostate Disease
As men get older, their chances of developing an enlarged prostate increase. More than half of men over 60 have an enlarged prostate, which grows to 80% by age 80. An enlarged prostate is a common symptom shared by three primary prostate diseases. Let’s explore these prostate diseases and how Radiology of Indiana is equipped to help with the diagnostic part of testing and diagnosis.
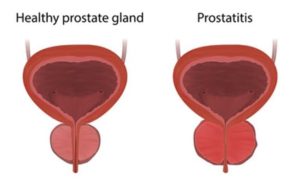
Types of Prostate Disease
Any man can develop a prostate problem. Here are the main three types of prostate diseases:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is when the prostate grows larger for reasons not related to cancer. It affects approximately 50% of all men before the age of 50 and more than 75% percent of men over 60.
- Symptoms include:
- Weak urinary stream
- A sense of not being able to empty the bladder completely
- Symptoms include:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Urinating more often or a sense of having to go right away
- Having to get up often at night to urinate
- Stopping and starting of the urine stream.
- Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate that a bacterial infection may cause. This disease may affect all ages of men and can occur in any prostate, whether enlarged or not. Symptoms of prostatitis are like those caused by an enlarged prostate and may include:
- Urge frequency
- Difficulty in emptying the bladder
- Chills
- Fever
- Pain or burning during urination
- Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of death due to cancer among men. Many prostate cancers grow slowly and are confined to the prostate gland. However, some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or no treatment. Other types are aggressive and can spread quickly. Prostate cancer symptoms include:
- Difficulty with beginning urination
- Frequent need to urinate, particularly at night
- Inability to urinate
- Weak or sporadic urine flow
- Painful or a burning sensation during urination
- Painful ejaculation
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Pain in the back, hips, or located in the extremities
Interventional and Traditional Imaging Capabilities
Radiology of Indiana has interventional and traditional imaging capabilities to meet your needs to assist in the evaluation and diagnosis of prostate diseases, including:
- Nuclear Medicine– A nuclear medicine procedure is a medical specialty that uses radioactive tracers (radiopharmaceuticals) to assess bodily functions and diagnose and treat disease.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)– An MRI scan can produce detailed images of the organs and tissues in the body.
- Prostatic Artery Embolization (PAE)– PAE is a minimally invasive procedure for the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). The prostate arteries are embolized by tiny microspheres that block some blood flow to the prostate, shrinking the tissue and relieving symptoms.
Dedication, Integrity, and Excellence
When you have physicians on staff with radiology experience dating back to 1960, adapting to the ever-changing healthcare environment becomes second nature. At Radiology of Indiana, our track record of exceptional services is what solidifies and strengthens our relationships with the hospitals, imaging centers, referring physicians, and patients who put their trust in us.
Let’s talk about how Radiology of Indiana can meet your needs too. Contact us today!
Sources:
https://utswmed.org/conditions-treatments/prostate-diseases/
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/prostate-problems
https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/benignprostate
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9100-benign-prostatic-enlargement-bph
https://med.virginia.edu/urology/for-patients-and-visitors/prostate-disease/