Celebrating Women’s Health Month: Advanced Imaging Services at Radiology of Indiana
May marks National Women’s Health Month, a time to prioritize the well-being of women and raise awareness about the essential healthcare services available. At Radiology of Indiana, we are deeply committed to supporting women’s health through a comprehensive suite of advanced imaging technologies. We understand that proactive care and early detection are paramount, and our state-of-the-art services are designed to provide you with the most accurate and detailed insights into your health.
This month, we celebrate the strength and resilience of women and reaffirm our dedication to providing compassionate and cutting-edge imaging services tailored to your unique needs. From revolutionary breast imaging techniques to minimally invasive interventional radiology procedures, ROI offers a modern approach to women’s healthcare.
Leading the Way in Breast Health with Advanced Imaging
Breast health is a cornerstone of women’s overall well-being, and early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes. At ROI, we offer a range of advanced breast imaging services designed to provide the most comprehensive assessment:
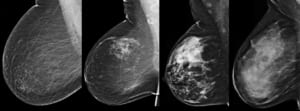
- 3D Mammography: Technology that goes beyond traditional 2D mammography by capturing multiple low-dose X-ray images of the breast from different angles. These images are then reconstructed into thin, three-dimensional slices, allowing our radiologists to see through overlapping tissue. This enhanced visualization significantly improves the detection of small cancers, reduces false positives, and provides greater clarity, especially for women with dense breast tissue.
- Breast MRI: Imaging that utilizes magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the breast. It is often used as a supplemental screening tool for women at high risk of breast cancer, to further evaluate abnormalities found on mammography or ultrasound, and to assess the extent of disease in diagnosed breast cancer. Our experienced radiologists are adept at interpreting breast MRI scans to provide crucial information for treatment planning.
- Breast Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses sound waves to create real-time images of the breast tissue. It is often used to evaluate breast lumps or abnormalities detected during a clinical breast exam or mammography. Breast ultrasound can help differentiate between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts and guide biopsies when necessary.
Our dedicated team of radiologists and technologists understands the sensitive nature of breast imaging and is committed to providing a comfortable, respectful, and supportive environment for every patient. We prioritize clear communication and ensure you feel informed and at ease throughout the process.
Interventional Radiology: Minimally Invasive Solutions for Women’s Health
Beyond diagnostic imaging, Radiology of Indiana offers innovative interventional radiology (IR) procedures that provide minimally invasive treatment options for various women’s health conditions, such as Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE).
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause a range of symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure on the bladder or bowel. Traditionally, treatment options for symptomatic fibroids often involved surgery, such as hysterectomy or myomectomy. However, UFE offers a less invasive alternative.
During a UFE procedure, our skilled interventional radiologists use real-time imaging guidance (fluoroscopy) to navigate a thin catheter through a small incision in the groin or wrist into the uterine arteries that supply blood to the fibroids. Tiny embolic particles are then released to block the blood flow to the fibroids, causing them to shrink and alleviate symptoms.
UFE offers several advantages over surgery, including:
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incision, leading to less pain and scarring.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Most women can return to their normal activities within a week or two, compared to several weeks for surgery.
- Uterus Preservation: UFE treats the fibroids while leaving the uterus intact, which is important for women who wish to preserve their fertility.
Your Partner in Women’s Health
At Radiology of Indiana, we are proud to offer these advanced imaging services as part of our commitment to women’s health. During National Women’s Health Month, we encourage all women to prioritize their health, schedule regular screenings, and learn about the options available to them. Our dedicated team is here to provide you with exceptional care, accurate diagnoses, and minimally invasive treatment options when needed.
Contact Radiology of Indiana today to learn more about our women’s imaging services and how we can partner with you on your journey to optimal health and well-being. We are here to empower you with the knowledge and advanced technology you deserve.